
 HOME
HOME CONTACT
CONTACT SUPPORT
SUPPORT SENSORYTEST.COM
SENSORYTEST.COM |
 HOME HOME CONTACT CONTACT SUPPORT SUPPORT SENSORYTEST.COM SENSORYTEST.COM |
|
Sensory testing professional's favorite virtual desktop. Say hello to SIMS Cloud Systems. From any device, any laptop, any iPad and even your cell phone. Log in from anywhere anytime. Inquire today. 
|
Mobile devices real test example Point your cell phone camera Easy for your respondents 
Link |
 VIEW REPORTS
VIEW REPORTS |
 QUESTION CHOICES
QUESTION CHOICES |
 TEST CHOICES
TEST CHOICES |
| INCOMPLETE BLOCK PAIRED COMPARISON EXAMPLES
Incomplete blocking such as 3C2, 4C2, 5C2, 6C2, 7C2, 8C2, etc. when Samples >=3, and presenting only two samples. |
Discrimination Paired Comparisons Incomplete Block Paired Comparisons View More Question Type Choices |
|
Incomplete block paired comparisons is also commonly referred to as multiple paired comparison, multiple paired preference, pairwise ranking, and incomplete block paired preference.
Panelist Ballot Example. The No Preference choice is optional 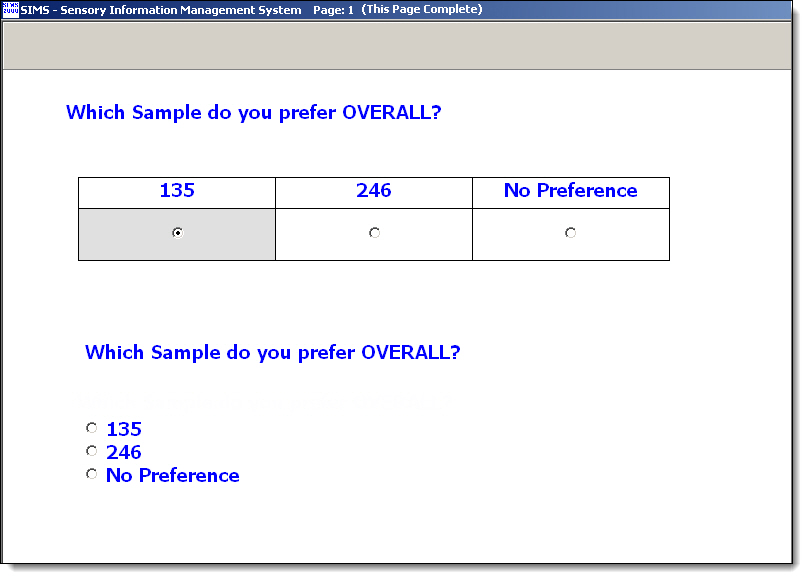
Primary method for doing Incomplete block paired comparison in your SIMS sensory panel software. - Hedonic; using SIMS hedonic attribute types, "select one", attribute seen with last relative sample. Alternative; Pairwise Ranking, SIMS ranking attribute type, "rank all". The rest of this webpage discusses the primary hedonic method. Questionnaire Set up the ballot as an Affective questionnaire using Hedonic attributes. Affective questionnaire will allow for more flexible Incomplete Block Experimental Design and Experimental Plan Rotations. Create an Hedonic attribute type with two choices and label the choices them with the following special TAGs.
The above example will present two choices with the blinding codes for the two samples in randomized order perfectly matching the Rotation Plan in the Test Definition. Example: Which Sample do you prefer OVERALL? ( ) 135 ( ) 246 Note: The "Attribute Seen With:" option should be set to "Relative Sample -- Last Sample", so that this question is only seen once at the end of the ballot. Note: Other handy TAGS are available as with all questions types in your SIMS sensory panel software. See the [Notes] buttons. Note: We have successfully tested this method with bigger BIB designs, such as 5C3, 8C4, etc., add some hedonic choices, see same reports. * See example Print screens shown below for Questionnaire Setup Experimental Design and Plan Set up your Experimental Design specifying the true absolute number of samples, which is 3 or more for incomplete blocks of PC tests. Select an Experimental Plan, such as Combination 3 choose 2, or create your own. Number of samples presented is always 2 for PC. The Design can be either a Balanced Incomplete Block (BIB) or an Unbalanced Incomplete Block (UBIB). In a BIB Design, there are m = t(t-1)/2 possible pairs, such as for a 3C2 test there are 3 possible pairs, 4C2 6 pairs, etc. In a BIB Design, to be completely balanced, all pairs must be seen equal number of times. And to eliminate order effect, also present each pair in reserve (m*2) You may need to create balanced SIMS Experimental Plan, example for 4C2, 12 pairs, 12 34 13 24 14 23 21 43 31 42 41 32. Create your Test Definition and review your Rotation Plan report in SIMS for accuracy. As always, "Test Your Test". Download Example, 4C2R1, n=48, Balanced Incomplete Block Paired Comparison (BIBPC), with No Preference option: SIMS software express package file: IBPC-EXAM.SIMS2000ExpressPackage.sql.ZIP SIMS software express package file, with panelist data: IBPC-EXAM-WITHDATA.SIMS2000ExpressPackage.sql.ZIP Reporting and Data This is an advanced type of question and setup, some attention to details is required for data interpretation. The raw panelist data saved is the actual 'return values', just like every hedonic question type in SIMS, therefore the raw data return values are *not* the Sample #s, they are positional orders. • SIMS Raw Data Export Report, by default, the columns for these hedonic questions will display the actual 'return values', not the sample selected.
• SIMS Data Frequency Reports will add additional report lines interpreting the data when these Special Hedonic Sample Choice Tags in Use is detected.
Example: This design was 4 samples. Balanced Incomplete Block Paired Comparison (BIBPC).
The experimental design was 4 samples, 2 presented, 1 reps. 4C2R1. 48 panelists and 48 pairs evaluated. Each panelist 1 pair.
Ballot PCN attribute included a No Preference option, see example print screen above.
Frequency Report:
Panelist selected frequency for each Absolute Sample:
Absolute Sample 1 Selected Frequency = 15 63% (15 out of 24 presentations)
Absolute Sample 2 Selected Frequency = 11 46% (11 out of 24 presentations)
Absolute Sample 3 Selected Frequency = 6 25% (6 out of 24 presentations)
Absolute Sample 4 Selected Frequency = 8 33% (8 out of 24 presentations)
No Prefer/Other Selected Frequency = 8 17% (8 out of 48 presentations)
The Frequency grid of Selected vs Non-selected Absolute Samples.
Read the grid from Left to Right.
Example: S1 selected over the S2, head-to-head, n times, and %.
vs | S1 | S2 | S3 | S4 |
-----------------------------------------------------------------
S1 | - | 4 (57%) | 6 (75%) | 5 (62%) |
S2 | 3 (43%) | - | 3 (60%) | 5 (83%) |
S3 | 2 (25%) | 2 (40%) | - | 2 (33%) |
S4 | 3 (38%) | 1 (17%) | 4 (67%) | - |
Summary of No Prefer/Other selected over any Sample presented.
No Prefer/Other selected over S1 & S2, head-to-head, Frequency = 1 13% (1 out of 8 presentations)
No Prefer/Other selected over S3 & S4, head-to-head, Frequency = 2 25% (2 out of 8 presentations)
No Prefer/Other selected over S2 & S4, head-to-head, Frequency = 2 25% (2 out of 8 presentations)
No Prefer/Other selected over S2 & S3, head-to-head, Frequency = 3 38% (3 out of 8 presentations)
Example: This design was Control vs 3 Tests. Unbalanced Incomplete Block Paired Comparison (UBIBPC). C vs T1 C vs T2 C vs T3
The experimental design was 4 samples, 2 presented, 3 reps. 4C2R3. 10 panelists and 30 pairs evaluated. Each panelist 3 pairs.
Frequency Report:
Panelist selected frequency for each Absolute Sample:
Absolute Sample 1 Selected Frequency = 14 47% (14 out of 30 presentations)
Absolute Sample 2 Selected Frequency = 5 50% ( 5 out of 10 presentations)
Absolute Sample 3 Selected Frequency = 4 40% ( 4 out of 10 presentations)
Absolute Sample 4 Selected Frequency = 7 70% ( 7 out of 10 presentations)
The Frequency grid of Selected vs Non-selected Absolute Samples.
Read the grid from Left to Right.
Example: S1 selected over the S2, head-to-head, n times, and %.
vs | S1 | S2 | S3 | S4 |
-----------------------------------------------------------------
S1 | - | 5 (50%) | 6 (60%) | 3 (30%) |
S2 | 5 (50%) | - | - | - |
S3 | 4 (40%) | - | - | - |
S4 | 7 (70%) | - | - | - |
Lower right cells are - because this example design was Control vs 3 Tests. C vs T1 C vs T2 C vs T3
• The SIMS sensory panel software Test Data Results Reports will add additional report lines interpreting the data when these Special Hedonic Sample Choice Tags in Use is detected. Example: Replication: 1
Sample Set: 1 Panelist: Anonymous Panelist ... saw block number: 1
Response: 1 Attribute: Sweetness Preference(Hedonic Scale)
Label(1) = 123 = <RELATIVE_SAMPLE_1_BLINDING_CODE>
Absolute Sample 1 was Selected, Sample description: Control
Panelist samples presented: 1-123 vs 2-246
• Advanced analysis, see SIMS Reports | Discrimination Reports | Paired Comparison Attribute Analysis - Select option: [X] Show Affective Incomplete Block PCs. Select your desired sample pair for analysis. • For additional advanced analysis, use your own Incomplete Block Paired Comparisons statistical calculations using the raw data and proper data interpretation. • Other reports in your SIMS sensory panel software may need to be scrutinized for proper data interpretation. |
|
Questionnaire Setup 
|
|
(The Scales on this Web page are not interactive.) References: Statistical Methods In Food and Consumer Research, Gacula, Singh, Bi, 2nd Ed, Chapter 11, pg 559 |
